Anatolia, a land of rich history, diverse culture, and breathtaking natural beauty, has captivated travelers and historians for centuries. Nestled in the heart of Asia Minor, this ancient region has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the birth of civilizations, and the convergence of cultures.
From the snow-capped peaks of the Taurus Mountains to the azure waters of the Mediterranean Sea, Anatolia’s diverse geography has shaped its history and influenced its people. The region’s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia has made it a melting pot of cultures, resulting in a vibrant tapestry of languages, religions, and traditions.
Anatolian Geography
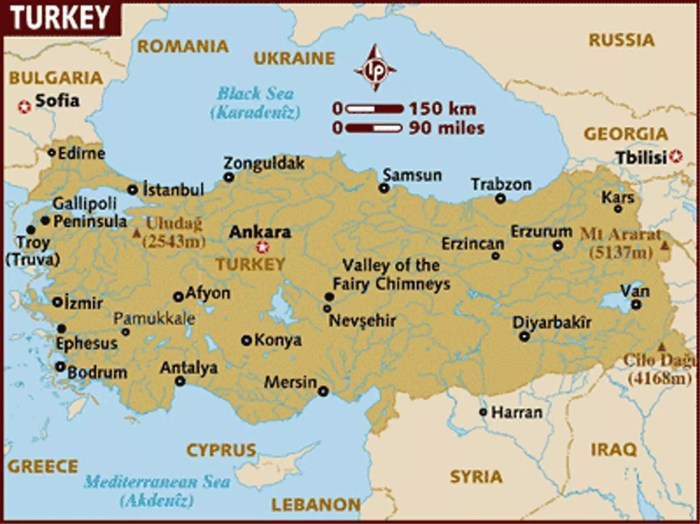
Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor, is a vast peninsula that forms the westernmost part of Asia. It is bordered by the Black Sea to the north, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean Sea to the west, and the Armenian Highlands to the east.
Anatolia is a land of great geographical diversity, with mountains, rivers, and plains. The most prominent mountain range is the Taurus Mountains, which run along the southern coast. The highest peak in Anatolia is Mount Ararat, which is located in the eastern part of the peninsula.
Anatolia, a land of ancient civilizations and diverse landscapes, invites travelers to explore its wonders. As you plan your journey, consider incorporating eco-friendly travel tips to minimize your impact on the environment. From using reusable water bottles to supporting local businesses that prioritize sustainability, your choices can make a difference.
Embracing these practices not only benefits Anatolia’s natural beauty but also enriches your travel experience.
Rivers, Anatolia
Anatolia is also home to several major rivers, including the Tigris, Euphrates, and Sakarya. These rivers have played an important role in the history and culture of the region.
Climate
The climate of Anatolia varies from region to region. The coastal areas have a Mediterranean climate, with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. The interior of the peninsula has a continental climate, with cold, snowy winters and hot, dry summers.
Influence on History and Culture
The geography of Anatolia has had a profound influence on its history and culture. The mountains have served as natural barriers, protecting the region from invasion. The rivers have provided water for irrigation and transportation. The climate has shaped the agricultural practices of the region.
Anatolian History
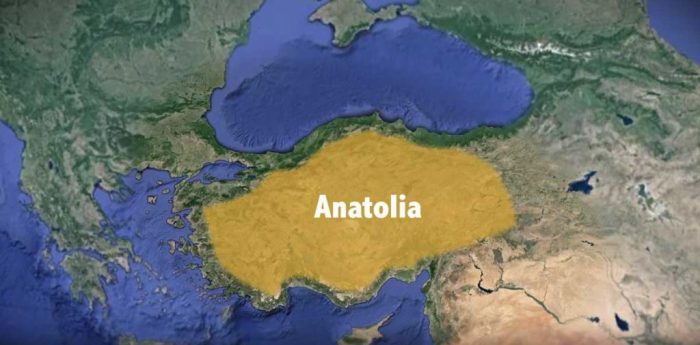
Anatolia, the land bridge between Europe and Asia, has a rich and complex history that has seen the rise and fall of numerous empires and civilizations. The region has been home to some of the world’s most influential cultures, including the Hittites, Greeks, Romans, and Ottomans.
Major Historical Events
- c. 1900 BCE: Hittites establish an empire in Anatolia, becoming one of the first great civilizations of the ancient world.
- c. 1200 BCE: The Hittite Empire collapses, and Anatolia enters a period of decline.
- c. 800 BCE: The Greeks begin to establish colonies in Anatolia, introducing their culture and language to the region.
- c. 546 BCE: The Persian Empire conquers Anatolia, bringing it under its control for over two centuries.
- 334 BCE: Alexander the Great conquers Anatolia, and the region becomes part of the Hellenistic world.
- 64 BCE: The Roman Empire conquers Anatolia, and the region becomes a province of Rome for over four centuries.
- 395 CE: The Roman Empire is divided into two halves, and Anatolia becomes part of the Eastern Roman Empire, also known as the Byzantine Empire.
- 1071 CE: The Seljuk Turks defeat the Byzantines at the Battle of Manzikert, and Anatolia becomes a Turkish stronghold.
- 1299 CE: The Ottoman Turks establish an empire in Anatolia, which will eventually become one of the most powerful empires in the world.
- 1453 CE: The Ottomans conquer Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire, and Anatolia becomes the center of the Ottoman Empire.
- 1923 CE: The Ottoman Empire collapses, and Anatolia becomes the Republic of Turkey.
Empires and Civilizations
Hittites
The Hittites were an Indo-European people who established an empire in Anatolia around 1900 BCE. The Hittites were a powerful and influential civilization, and their empire lasted for over four centuries. The Hittites were known for their advanced military technology, including the use of iron weapons and chariots.
Greeks
The Greeks began to establish colonies in Anatolia around 800 BCE. The Greeks introduced their culture and language to the region, and Anatolia became a center of Greek civilization. The Greeks established many important cities in Anatolia, including Ephesus, Smyrna, and Miletus.
Romans
The Roman Empire conquered Anatolia in 64 BCE. The Romans brought peace and prosperity to the region, and Anatolia became a wealthy and important province of the Roman Empire. The Romans built many roads, bridges, and aqueducts in Anatolia, and they also introduced Christianity to the region.
Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks established an empire in Anatolia in 1299 CE. The Ottoman Empire was one of the most powerful empires in the world, and it lasted for over six centuries. The Ottomans were known for their military prowess, and they conquered a vast territory that included much of southeastern Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa. The Ottomans also made significant contributions to art, architecture, and literature.
Anatolian Culture
Anatolia is a melting pot of cultures, having been influenced by many different civilizations throughout history. The region is home to a diverse range of languages, religions, and traditions.
The languages of Anatolia belong to several different language families. The most widely spoken language is Turkish, which is an Altaic language. Other major languages include Kurdish, Arabic, and Armenian. Anatolia is also home to a number of minority languages, such as Laz, Circassian, and Chechen.
The religions of Anatolia are equally diverse. The majority of the population is Muslim, but there are also significant populations of Christians, Jews, and Zoroastrians. Anatolia has been a center of religious pilgrimage for centuries, and many of its cities are home to important religious sites.
The traditions of Anatolia are as varied as its languages and religions. The region is known for its rich folklore, music, and dance. Anatolian cuisine is also highly distinctive, and many of its dishes have become popular around the world.
Cultural Influences
The different cultures of Anatolia have influenced each other over time. For example, the Turkish language has been influenced by Arabic, Persian, and Greek. The music of Anatolia has been influenced by both Eastern and Western traditions. And the cuisine of Anatolia has been influenced by the cuisines of many different cultures.
The cultural diversity of Anatolia is a source of great strength for the region. It has allowed Anatolia to become a crossroads of civilizations and a center of cultural exchange.
Anatolian Cuisine
Anatolian cuisine is a rich and diverse culinary tradition that has been shaped by the many cultures that have lived in the region over the centuries. The cuisine is characterized by its use of fresh, seasonal ingredients and its reliance on simple, traditional cooking methods.
Some of the most popular traditional dishes in Anatolian cuisine include:
- Kebabs: Grilled or roasted meats that are typically served with rice or bread.
- Lahmacun: A thin, crispy flatbread that is topped with ground meat, vegetables, and spices.
- Börek: A flaky pastry that is filled with cheese, meat, or vegetables.
- Dolma: Stuffed vegetables, such as peppers, tomatoes, and eggplant.
- Baklava: A sweet pastry that is made with layers of filo dough, nuts, and honey.
Anatolian cuisine has been influenced by the many different cultures that have lived in the region, including the Greeks, Romans, Persians, Arabs, and Turks. This has resulted in a cuisine that is both diverse and flavorful.
Ingredients
The ingredients used in Anatolian cuisine are typically fresh and seasonal. Some of the most common ingredients include:
- Vegetables: Tomatoes, onions, peppers, eggplant, and zucchini are all commonly used in Anatolian cuisine.
- Fruits: Grapes, figs, apricots, and pomegranates are all popular fruits in Anatolia.
- Meat: Lamb, beef, and chicken are the most commonly used meats in Anatolian cuisine.
- Dairy: Yogurt, cheese, and milk are all important dairy products in Anatolian cuisine.
- Spices: Spices such as cumin, coriander, paprika, and mint are commonly used in Anatolian cuisine.
Anatolian Art and Architecture
Anatolia has a rich artistic and architectural heritage, reflecting the diverse cultures that have inhabited the region throughout history. From the Neolithic period to the present day, Anatolia has been a melting pot of artistic influences, resulting in a unique and diverse artistic tradition.
The earliest known art from Anatolia dates back to the Neolithic period, and includes pottery, figurines, and other artifacts. During the Bronze Age, Anatolia was home to several major civilizations, including the Hittites, who developed a distinctive style of architecture characterized by massive stone walls and gateways. The Phrygians, who succeeded the Hittites, were known for their elaborate metalwork and jewelry.
In the Classical period, Anatolia was ruled by the Greeks and Romans, who introduced their own artistic styles to the region. Greek temples and theaters can still be found in many parts of Anatolia, while Roman roads and aqueducts are a testament to the region’s infrastructure. The Byzantine Empire, which ruled Anatolia from the 4th to the 15th centuries, left behind a legacy of churches and monasteries, many of which are still in use today.
After the Seljuk Turks conquered Anatolia in the 11th century, they introduced a new style of architecture to the region, characterized by pointed arches and domes. The Ottomans, who succeeded the Seljuks, continued to develop this style, and built some of the most famous mosques and palaces in the world, including the Hagia Sophia in Istanbul.
Modern Anatolian Art
In the 20th century, Anatolian art began to move away from traditional styles and embrace modernism. Turkish artists such as Fahrelnissa Zeid, Bedri Rahmi Eyüboğlu, and Abidin Dino were pioneers of the modern art movement in Turkey, and their work has had a major influence on subsequent generations of artists.
Today, Anatolian art is a vibrant and diverse field, with artists working in a wide range of styles and media. From traditional crafts to contemporary installations, Anatolian art continues to reflect the region’s rich cultural heritage.
Anatolia, a historical and cultural hub, boasts diverse landscapes that extend beyond its ancient ruins. For those seeking underwater adventures, Anatolia offers an array of scuba diving locations , where crystal-clear waters reveal vibrant marine life and underwater wonders. Whether exploring the Aegean coast or the Mediterranean depths, scuba diving in Anatolia unveils the hidden treasures of this captivating region.
Anatolian Natural Resources
Anatolia is rich in natural resources, including minerals, water, and land. These resources have been used to develop the region’s economy and support its population.
Minerals
Anatolia is home to a variety of minerals, including iron, copper, gold, silver, and lead. These minerals have been mined for centuries and have played a major role in the development of the region’s economy. Iron ore is found in the Divriği area of Sivas province, and copper is mined in the Ergani area of Diyarbakır province. Gold and silver are found in the Bergama area of İzmir province, and lead is mined in the Keban area of Elazığ province.
Water
Anatolia has a number of rivers and lakes, which provide water for irrigation, drinking, and transportation. The Tigris and Euphrates rivers are two of the most important rivers in the region, and they provide water for irrigation in the southeastern Anatolia region. The Atatürk Dam on the Euphrates River is one of the largest dams in the world, and it provides water for irrigation and hydroelectric power generation.
Land
Anatolia has a variety of landforms, including mountains, plateaus, and plains. The mountains provide grazing land for livestock, and the plateaus and plains are used for agriculture. The Konya Plain is one of the largest plains in Anatolia, and it is known for its fertile soil and agricultural production.
Anatolia, with its rich history and captivating landscapes, beckons travelers seeking an extraordinary journey. If you desire the ultimate indulgence, consider exploring luxury travel deals that cater to discerning tastes. Immerse yourself in Anatolia’s ancient ruins, marvel at its stunning natural wonders, and savor the region’s exquisite cuisine, all while enjoying the unparalleled comfort and exclusivity that luxury travel offers.
Anatolian Tourism
Anatolia, with its rich history, diverse culture, and breathtaking natural landscapes, is a popular tourist destination. From ancient ruins to stunning coastlines, there’s something for everyone in this fascinating region.
Historical Sites
Anatolia is home to some of the world’s most iconic historical sites, including the ruins of Troy, Ephesus, and Pergamon. These ancient cities offer a glimpse into the region’s rich past and are a must-see for history buffs.
Natural Wonders
Anatolia is also blessed with an abundance of natural beauty. The region is home to towering mountains, crystal-clear lakes, and stunning coastlines. Visitors can enjoy hiking, swimming, and boating in some of the most beautiful scenery in the world.
Cultural Experiences
In addition to its historical and natural attractions, Anatolia is also known for its vibrant culture. Visitors can experience traditional Turkish music and dance, visit local markets, and learn about the region’s unique customs and traditions.
Economic Impact of Tourism
Tourism has played a significant role in the development of Anatolia’s economy. The industry has created jobs, boosted infrastructure, and helped to preserve the region’s cultural heritage. In recent years, Anatolia has become increasingly popular with tourists from all over the world, and the industry is expected to continue to grow in the years to come.
Final Wrap-Up
Anatolia’s legacy continues to inspire and intrigue, offering a glimpse into the past and a testament to the enduring spirit of human civilization. Its rich history, diverse culture, and natural beauty make it a destination that captivates the imagination and leaves an unforgettable mark on every visitor.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the geographical significance of Anatolia?
Anatolia’s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia has made it a vital trade route and a meeting point for different cultures throughout history.
What are some of the major historical events that have occurred in Anatolia?
Anatolia has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, including the Hittite, Greek, Roman, and Ottoman empires, leaving behind a rich legacy of historical sites and cultural heritage.
What are the main cultural influences that have shaped Anatolia?
Anatolia’s culture is a blend of influences from the Middle East, Europe, and Asia, resulting in a diverse tapestry of languages, religions, and traditions.
What are some of the traditional dishes of Anatolian cuisine?
Anatolian cuisine is renowned for its flavorful dishes, including kebabs, börek, dolma, and güllaç, which reflect the region’s rich culinary heritage.
What are some of the most popular tourist attractions in Anatolia?
Anatolia boasts a wealth of tourist attractions, including ancient ruins, historical cities, stunning natural landscapes, and vibrant cultural experiences.